In the complexity of tick-borne and opportunistic infections, ArminLabs specializes in T-cellular tests (EliSpot), B-cellular tests (IgA, IgM and IgG-antibodies), and NK cell tests (CD57, CD56) for several bacterial, viral, parasitic, and fungal infections.
The best-known tick-borne infection is named Lyme disease or Lyme Borreliosis, an infection by Borrelia burgdorferi after tick or insect bites.
Diagnostic tests for coinfections like Ehrlichia/Anaplasma, Rickettsia, Bartonella and Babesia play an increasingly important role in the diagnosis and treatment of patients.
Laboratory tests for Chlamydia, Mycoplasma, Coxsackie-Virus, EBV, CMV, HSV, and HHV6 infections are essential in the complexity of multiple infections.
Together with Gärtner laboratories (Limbach group SE) ArminLabs is able to offer you the following categories of diagnostics:
Specialization in multiple chronic infections
Immune dysfunction
Inflammation
Environmental toxins
Hormones
Mitochondrial dysfunction
Allergies
Gastrointestinal health
ArminLabs Tick-borne Disease Services & Testing
-
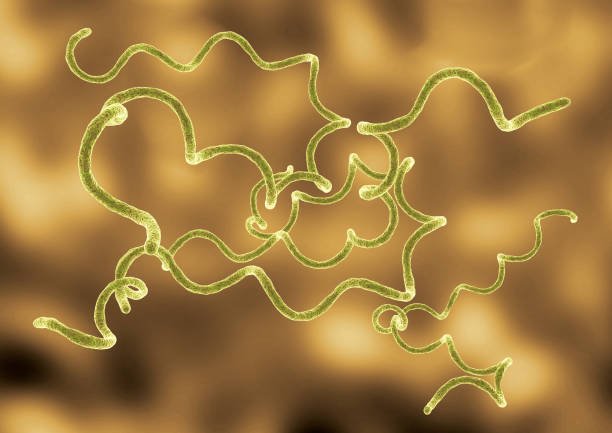
Lyme Borreliosis
Lyme disease is an inflammatory disease, which involves multiple body systems and causes symptoms that mimic other diseases. Beginning with a bull’s eye rash (around 50 % of all infections), it progresses to flu-like symptoms, and can lead to arthritis or many other symptoms. If left untreated, Lyme disease can progress to symptoms as serious as encephalitis, cardiomegaly, and inflammation of the pericardium and sensory nerves.
-

Ehrlichia & Anaplasma
These obligate intracellular bacteria are both epidemiologically and etiologically distinct from one another. At present, five strains capable of infecting humans have been identified and three (Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Ehrlichia chaffeensis and Ehrlichia ewingii) have been clinically characterized. Neither Ehrlichia canis nor Nerorickettsia sennetsu, the remaining human strains, have been sufficiently investigated.
-

Bartonella
Bartonella species are vector-transmitted, blood-borne, intracellular, gram-negative bacteria that can induce prolonged infections in the host. . There are several species capable of causing infections in humans, especially Bartonella henselae and Bartonella quintana. Persistent infections of humans and animals (domestic and wild) result in a substantial reservoir of Bartonella organisms in nature, which can serve as a source for inadvertent infection of humans.
-

Babesiosis
Nearly 100 species within the genus Babesia have been described, of which several are capable of infecting humans. Human Babesiosis is a life-threatening, emergent tick-borne disease, caused primarily by Babesia microti, though human infections with Babesia gibsonii, Babesia WA1 and CA1 have also been reported. Poor detection may explain such low statistics, implying undetected positive cases could be largely superior.
-
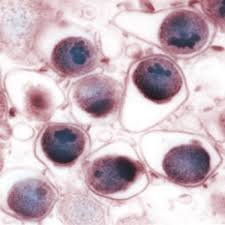
Chlamydia pneumoniae
This atypical bacterium commonly causes pharyngitis, bronchitis, coronary artery disease and atypical pneumonia in addition to several other possible diseases including atherosclerosis. Also, the bacteria would play an important role in the exacerbation of asthma. It is found in nearly 60 % of asthmatic children between the ages of 5 and 15 years, and there is a direct link between the importance of the immune response against Chlamydia and the frequency of seizures.
-

Chlamydia trachomatis
Chlamydia trachomatis is an obligate intracellular bacterium, gram negative. This bacterium is responsible for Chlamydia (or chlamydia) urethritis, a sexually transmitted disease that is most common in Latin America and the USA after Papillomavirus (50 times more frequent than gonorrhea, which is more common than syphilis). Its reservoir is strictly human.
-

Mycoplasma
The bacteria Mycoplasmas are now known as the smallest free-living, self-replicating, fastidious bacteria. Their lack of a cell-wall also renders traditional cell-wall active antibiotics useless. Mycoplasma species, including Mycoplasma fermentans, have been identified in blood-sucking arthropods. One representative are Ixodes ticks, which also transmit Lyme disease, Babesiosis, Ehrlichiosis, and Bartonellosis.
-

Yersinia
Yersinia is a genus of bacteria in the family Yersiniaceae. Its species are Gram-negative, coccobacilli bacteria, a few micrometers long and fractions of a micrometer in diameter, and are facultative anaerobic. Some members of Yersinia are pathogenic in humans, such as Yersinia enterocolitica, Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia pestis. Rodents are the natural reservoirs of Yersinia, less frequently, other mammals serve as hosts. Yersinia species are further found in soil and waters.
-

Rickettsia
The rickettsiae (Rickettsia) form a kind of bacteria of the family Rickettsiaceae and the tribe Rickettsieae. Rickettsiae are, like chlamydia, compulsory intracellular parasite bacteria of small size (300 nm). They live in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. They are mainly found in arthropods which are their vectors (especially haematophages: ticks, lice and mites) causing various diseases in humans and animals (Rickettsiosis).
-

Yeast and Mould
Yeast and mold can cause any number of symptoms including: Oropharyngeal candidiasis (thrush), vaginal candidiasis, systemic: abscess, thrombophlebitis, endocarditis, infections of the eyes and other organs. Candida albicans is part of the normal flora of the mucous membranes of the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and female genital tracts but when overgrowth from antibiotics or immune suppression occurs it can become problematic
-

Viruses
A virus is made up of a core of genetic material, either DNA or RNA, surrounded by a protective coat called a capsid which is made up of protein. Sometimes the capsid is surrounded by an additional spikey coat called the envelope. Viruses are capable of latching onto host cells and getting inside them.
Available Virus Tests Include: EBV, CMV, HSV 1/2, VZV, Coxsackievirus, HHV6, HHV7, HHV8, TBE, Enterovirus, Parvovirus, Echovirus
-

Parasites
A parasite is an organism that lives in, on, or with another organism, called a host, and feeds off of it for survival. Parasites can harm their host in various ways, such as by feeding, growing, or multiplying.
Available Parasite Tests Include: Toxoplasmosis, Echinococcus multilocularis, Entamoeba histolytica, Leishmania infantum, Taenia solium, Toxocara canis, Trichinella spiralis
Consultation for doctors and naturopaths
ArminLabs offers consultations for doctors and naturopaths. They can assist in the selection and explanation of laboratory tests, the interpretation of test results, and in general questions about therapies.
US Patients: Order Your ArminLabs Testing from Alianaza BioHealth
Since its inception Alianza Biohealth has always been looking for ways to bring innovative health solutions through laboratory testing that is not commonly available to practitioners and patients in North and Latin America. Home Tests can be ordered from Alianza BioHealth for US and South American patients as well.
Armin Schwarzbach, MD, PhD
Dr. Armin Schwarzbach, Medical Doctor and Specialist of Laboratory Medicine, founder of ArminLabs in Augsburg/Germany, has been at the forefront of tick-borne research for more than 25 years and is an expert in diagnosing and treating infectious diseases. He is an Advisory Board member of AONM London, England, and Board Member of the German Borreliosis Society and Member of the German Society of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine. Dr. Schwarzbach has experiences in biochemistry, pharmacy, hormones, immunology, infectious diseases, oncology, internal medicine and did his PhD in the development of the first Radioimmunoassay for hGIP. He has served as an expert on advisory committees on Lyme Disease in Australia, Canada, Ireland, France, England, Sweden and Germany.